Microwaves and ovens play very similar roles. You can cook, reheat, and defrost food in both appliances. So, surely, that means microwave-safe containers are oven-safe, and vice versa, right? Actually, no.
Microwave-safe containers are not always oven-safe and vice versa. For instance, a takeout box is microwaveable but will burn in an oven. Another example is tempered glass, which is safe to use in an oven but will most likely shatter in a microwave due to thermal shock.
In this guide, I’ll explain the differences in how microwaves and ovens work, why microwave-safe containers are not always oven-safe, and what sort of cookware materials are ideal for each of these appliances.
Microwave vs. Oven
One look at a microwave and an oven, and you should immediately tell how different they are. That said, they serve very similar purposes, such as both appliances can reheat food, can be used to cook raw food, or can defrost food.
However, that’s where the similarities end. For the most part, a microwave is unlike an oven and vice versa. Allow me to explain.
How does a microwave work?

Microwaves, or microwave ovens, use microwave radiation to heat water. The microwaves penetrate the surface of food and cause the moisture particles to vibrate violently. When this happens, the moisture heats up, which causes the temperature of the food to rise. Over time, the food’s own juices will cook itself.
One of the biggest differences between microwaves and ovens is how they treat water. If you insert a glass of water into a microwave, there’s a good chance that the water will literally explode. In an oven, the water will evaporate with time.
How does an oven work?

Ovens, on the other hand, do not rely on mysterious radiation to heat up and cook food. Instead, they introduce direct heat to your food, which cooks the surface and eventually penetrates the inside, regardless of whether or not the food contains moisture already.
The source of heat comes from coils that heat up by the power of electricity or an open flame that is fueled by a consistent flow of gas. As such, you can use an oven to sear food and crisp up the exterior. A microwave, on the other hand, won’t achieve the same crispy results.
Does Microwave-Safe Mean Oven-Safe?
Many times, you can find a label on the side or underside of cookware that tells you whether or not it is microwave-safe or oven-safe. You should always look for the label before sticking the container in a microwave or oven.
But if you find the microwave-safe label on the food container, does that mean it’s safe to use in an oven? Not necessarily.
There are a few key differences between microwave-safe and oven-safe dishes, which I’ll describe below.
What makes a dish microwave-safe?
First and foremost, a microwave-safe container is one that has a heat tolerance of up to 250°F since microwaves can heat up food to only 212°F (the boiling point of water). However, most, if not all, oven-safe bakeware has a heat tolerance that is far greater than this.
Another thing to take note of is how the material reacts to microwave radiation. Microwave radiation won’t just fail in penetrating the surface of metal containers, but it can also lead to “arcing,” which can quite possibly create a fire inside the microwave.
Finally, microwaves heat up moisture quickly. The heat can transfer to the cooking vessel, and if it’s not designed to withstand sudden changes in temperature, it will most likely crack, shatter, or become warped in some way. Basically, a microwave-safe container must be able to withstand rapid changes in temperature.
What makes a dish oven-safe?
The only prerequisite for a container to be oven-safe is that it must be able to withstand the internal temperature of an oven. That sounds simple enough until you check the temperature setting of your oven. Usually, ovens have a maximum heat setting of 450 to 500°F, which is more than twice as hot as the water gets in a microwave.
Thermal resistance is another important aspect of oven-safe materials. Basically, the bakeware should not break under thermal shock. This pretty much includes most of the cookware materials we’re all used to, including metal, tempered glass, and stone.
What Materials Are Safe to Use in a Microwave or an Oven?
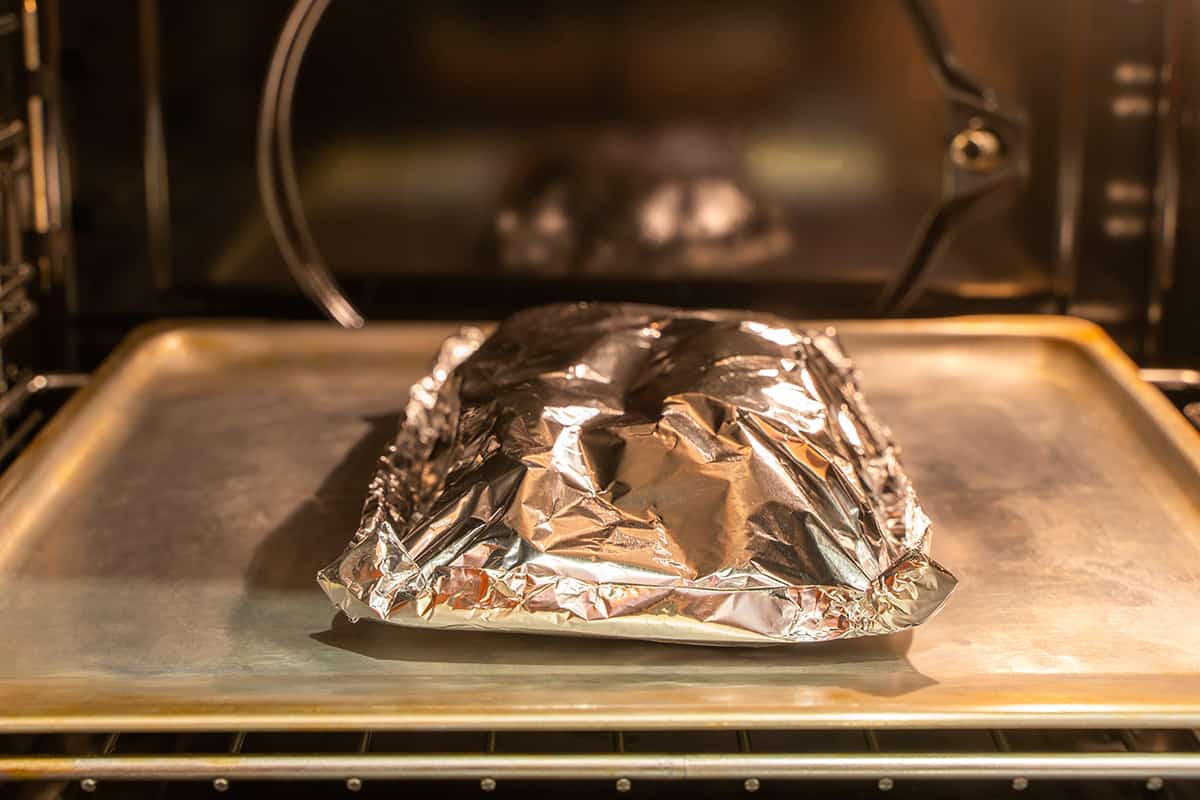

Now, let’s go over the different types of cookware materials. Below, I’ll explain what each of them is and whether or not it’s safe to use in a microwave or an oven.
Aluminum
One of the most widely used metals for cookware is aluminum for its heat conduction and low cost. Many of you guys might have at least one aluminum pot or pan in your home, which you use almost every day when cooking on a stovetop.
The good thing about aluminum, apart from its semi-durability and excellent heating capabilities, is that you can transfer it from a cooktop to an oven and vice versa. However, aluminum, along with other metals, should not go inside a microwave.
Aluminum foil
Aluminum foil is not really considered to be a cooking dish. However, in a pinch, you can fold and crinkle aluminum foil to create a makeshift baking dish that can hold a tiny bit of moisture. Like aluminum pots and pans, aluminum foil is safe to use in an oven—in fact; many people use it for tenting their foods to prevent them from drying out. However, again, you should not put it in a microwave.
Stainless steel
Stainless steel mixing bowls, pots, and pans, which are all oven-safe, are almost identical to aluminum in every way. It is an excellent heat conductor, so it will cook your food evenly while it bakes in an oven. However, you will have to pay top dollar for a stainless-steel pan or pot since they’re more durable than aluminum.
Plastic
Perhaps for most of us, most of our drinkware and dishes are made of plastic. You also probably know through experience that plastic doesn’t have a high thermal resistance since it can melt when it’s placed too close to a source of heat. So, it does not belong in an oven.
And nor does it belong in a microwave! The chemicals that go into making plastic can react to the heat from your food, which isn’t good for your health.
Teflon
Teflon is a nonstick coating added to the insides of pots, pans, and other cookware. It can withstand temperatures of up to 500°F, making them, for the most part, oven-safe. However, avoid using it underneath your broiler, which can exceed 550°F in many oven models.
This material is considered safe to use in a microwave, but the metal base on which it adheres is not. So, you should try and avoid microwaving or even baking with Teflon-coated cookware.
Ceramic
Ceramic cookware is made with organic materials—mostly clay. Before making it to retail stores, ceramic cookware undergoes a tempering process that increases its structural integrity, allowing it to withstand extreme changes in temperature. As such, ceramic is completely safe to use in an oven.
However, the same ceramic dish may not be microwave-safe. Make sure the dish has a microwave-safe label on it before trying to cook with it in your microwave.
Tempered glass
Tempered glass, such as Pyrex, undergoes multiple heating and cooling processes to make it durable and more resistant to thermal shock. It is ideal for baking, but you should make sure that you don’t stick a cold glass casserole dish in a preheated oven (remember thermal shock?).
The thermal shock principle is also what makes it inappropriate for microwaving. Since microwave radiation heats moisture up rapidly, there’s a good chance that heated water molecules will transfer to the dish, causing it to shatter inside the microwave.