One of the most common and essential ingredients used in most household recipes is vegetable oil. Have you ever bought vegetable oil in enormous quantities and thought of how to store them? You are not alone.
Many people are confused about the proper method for storing vegetable oil and if freezing vegetable oil will have any effect because of the cold temperatures. This is because, like you, they don’t want their oil to go bad.
But is freezing vegetable oil possible? Continue reading to learn more about freezing vegetable oil, how, and why.
Does vegetable oil freeze? The answer is yes. At the right temperature and with the proper process, you can freeze vegetable oil. Freezing vegetable oil has proven to be a good way of preserving vegetable oil and prolonging its shelf life.
Don’t worry about the vegetable oil losing its consistency or use due to cold temperatures. It goes back to normal as if nothing ever happened when heated. I’ll tell you more about it in this article.
Vegetable Oil: Uses and Ingredients
There are so many uses for vegetable oil, some of which you may not know about. The oil is not only used for cooking or frying as popularly believed.
Vegetable oil is very important in many recipes and its other use cases. Because of this, it’s advisable to get them in large portions.
Buying them in large quantities will raise how to store them. Not just store them, but in a way, it can still be helpful after a very long time and preserve the ingredients inside them.
What are the uses of vegetable oil, and what is it made of?
Uses of Vegetable Oil
What do you use your vegetable oil for? Cooking! Frying! Greasing! What else?
Did you know that these are not all the uses of vegetable oil?
Yes! Vegetable oil is used chiefly for cooking, greasing, and frying. But these are not the only uses of vegetable oil. Vegetable oil can be used as a moisturizer or a hair conditioner, even though cooking, greasing, and frying are just the common uses.
Let’s look at the common and uncommon uses of vegetable oil.
Common Uses
- Cooking foods like fried rice, curry rice, sauce, stew, etc.
- Frying foods or proteins like beef, mutton, chicken, pork, and any other meats
- Baking practices and greasing baking pans
- Boosting fire in grills
- Removal of rusts
Uncommon Uses
- Fuel in most oil lamps, especially the archaic ones
- Used as a seasoning for nonstick kitchenware and cookware, including cast iron
- Removing hard-to-remove splinters, labels, or stickers
- Hair conditioner and feet moisturizer
Vegetable Oil Ingredients
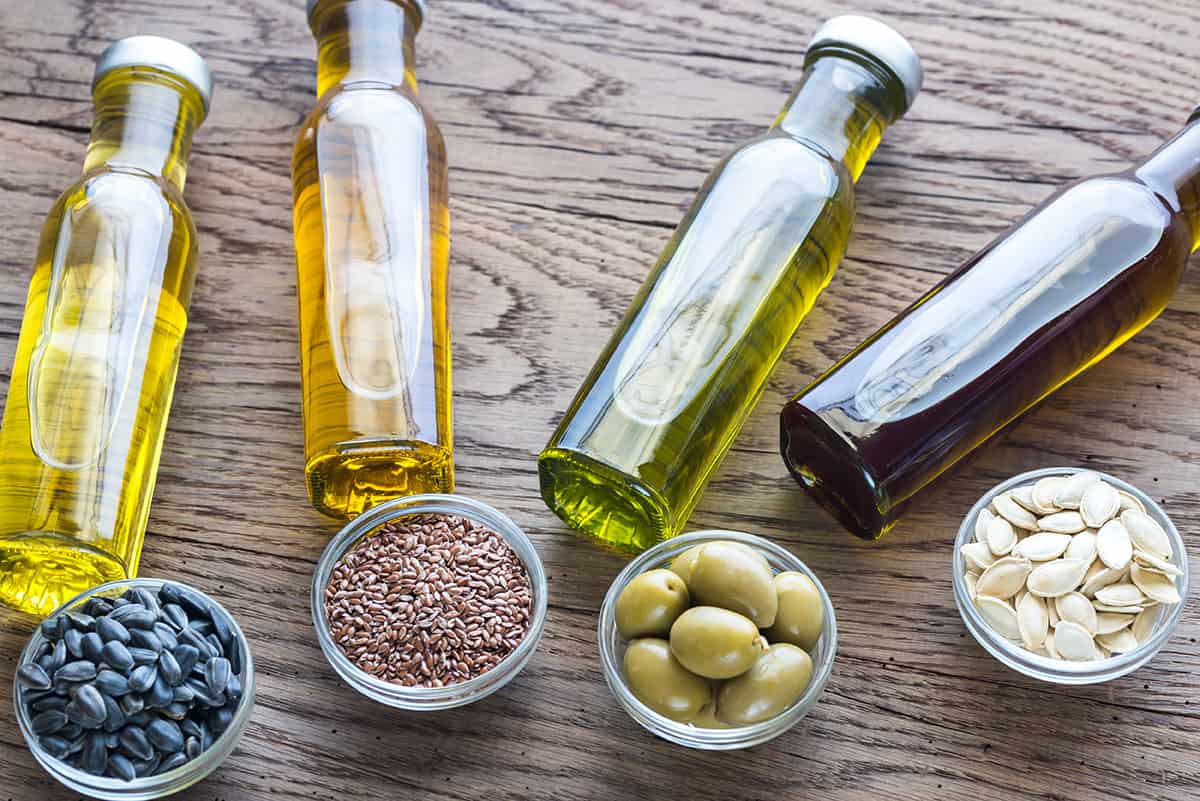

Most vegetable oils are made from a combination or solution of various ingredients which are brought together in different proportions. These ingredients can vary from different kinds of fruits and vegetables.
Some vegetable oils are not only made with fruits and vegetables but also with oils that come from specific seeds.
All these ingredients or triglyceride mixtures are mixed up to form the vegetable oil we know. Which is a transparent and slightly viscous solution that is liquid when left at room temperature.
Triglycerides are the main contents of natural fats and oils. It is an ester which consists of three fatty acids and one glycerol.
Sometimes, most vegetable oil manufacturers add some additives to the oil during the making process. These additives influence the properties and behavior of vegetable oils and may affect their freezing. Either by increasing their freezing point or reducing it.
However, some brands of vegetable oil are purer than others. Examples of very pure vegetable oil include:
- Canola oil
- Coconut oil
- Grapeseed oil
- Olive oil
- Peanut oil
- Sunflower oil and many others.
Vegetable Oil Freezing and Other Storage Options
There are different ways to store your vegetable oil. But one of the best ways is to freeze vegetable oil.
Although vegetable oil does not actually freeze in the true sense of the word freeze. But it is preserved by the very cold temperatures. And will last longer and appear more vicious and solid.
There are specific steps you need to take to achieve this. I will show you all those very soon.
Most vegetable oils, especially the very pure ones like coconut oil, do not behave as stated above. Coconut oil freezes, unlike vegetable oil, bought in grocery stores. It freezes by forming crystals which arise as a result of the fatty acids or triglycerides molecular structure.
Freezing vegetable oil will not affect the integrity of the oil. So there’s no need for you to worry. Most times, when you place the oil in the freezer, you might notice that the constituents in the oil begin to separate.
At this point, you might feel that the oil is bad or can’t be used again. But this is normal for most vegetable oils.
Once heated, the oil returns to its normal consistency as if nothing ever happened.
What is the Freezing Point of Vegetable Oil?
Naturally, everything that can freeze freezes at a particular temperature. It is known as the freezing point of that substance.
For most vegetable oil, the freezing point is any temperature below 40 degrees Fahrenheit. In comparison, some will only freeze at temperatures below 10 degrees Fahrenheit.
Freezing is not the only method for preserving vegetable oil. Vegetable oil can also be refrigerated or placed in the pantry.
Pantry
Some vegetable oil can be stored in pantries that are cool, dry, and not in contact with direct sunlight.
They should be kept away from humidity, warm temperatures, and direct sunlight, which affects vegetable oils. It causes them to break down and quickly become rancid.
Refrigerator
Some vegetable oils are more delicate than others. These oils need cooler temperatures for preservation to retain their freshness.
While in the refrigerator, these oils might become very dense and cloudy but not frozen. This does not mean the oil is bad. Once heated, it regains its normal texture.
These three different methods can be combined or used independently to preserve your vegetable oils.
How to Freeze Vegetable Oil
The processing of freezing vegetable oil is quite simple and not complicated at all. It does not require any particular skill or prior knowledge. And it’s not even something special.
But because I promised to show you everything about preserving vegetable oil by freezing it, I will also mention how.
First Step: Storing the Vegetable Oil
The first step in the process of freezing vegetable oil is getting an airtight container to store the oil in. This would be needed if the original container of the oil had been misplaced or damaged.
Second Step: Ensure the Container is Tight
Make sure that the new container or the original container of the oil is well sealed with no opening whatsoever.
Third Step: Place Container in the Freezer
This is the final process, and it involves putting the well-sealed and airtight container of vegetable oil into a freezer.
Importance of Freezing Vegetable Oil
When stored in the right way, Vegetable oil can be reused for a longer time. Throwing vegetable oil is not only harmful or wasteful to the environment. It is also wasteful fiscally.
Freezing vegetable oil helps you stay budget-conscious and environmentally friendly. Even after freezing your vegetable oil for a very long time, you can still use it to make meals as delicious as the first time. Or use it for whatever purpose you decide.
Properly freezing your vegetable oil in airtight and well-sealed containers will help you stave off Oxidation. A process that is like the bane of all kinds of vegetable and cooking oil.
What’s Oxidation, and how does it affect Vegetable oil?
Oxidation occurs in vegetable oil when they are exposed to heat and light. This causes the bonds in the oil to break, affecting the oil’s integrity.
When this happens, vegetable oil produces some harmful compounds and byproducts that cause a rancid taste when you use harmful oils.
Although different vegetable oils undergo Oxidation at different levels of exposure, freezing your vegetable oil will prevent it from happening.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Freezing Vegetable Oil
On earth, everything with advantages has accompanying disadvantages. Although sometimes the advantages outweigh the disadvantages.
Before going over the disadvantages, let’s look at some of the advantages of freezing vegetable oil.
Advantages of Freezing Vegetable Oil
- Increases the oils shelf life by two years
- It is a very simple process
- The steps in freezing vegetable oil are not complicated and can be done by anyone.
- Freezing does not affect the texture or integrity of the vegetable oil
- Using the oil after freezing is not tricky. Once introduced to heat, the oil returns to the initial consistency.
Disadvantages of Freezing Vegetable Oil
- The vegetable oil will not actually freeze in the real sense of the word. However, it will stay preserved for you as long as possible.
- You might notice a slight change in the consistency of the oil when it is removed. This is, in fact, a fixable con. All you need is a little heat to set things right.






