You’re probably familiar with almost all parts of a stove. However, have you ever heard the term “stove eye” before? It might be confusing, especially since there’s no part of the stove that helps you “see” anything.
The “stove eye” is the part of the stove where heat is produced—a.k.a., the burner. This term is usually associated with certain stoves brands. It generates heat by either electricity or gas, where heat is regulated via a control knob.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of stove eyes. We’ll explore the science behind their operation, different types of stove eyes, their safe and efficient usage, and common problems and fixes.
The Science Behind How a Stove Eye Works
The functioning of a stove eye involves a bit of science. It’s all about how we harness and control energy to cook our food. The two most common types of stove eyes are electric and gas, and both work a little differently.
Electric stove eyes
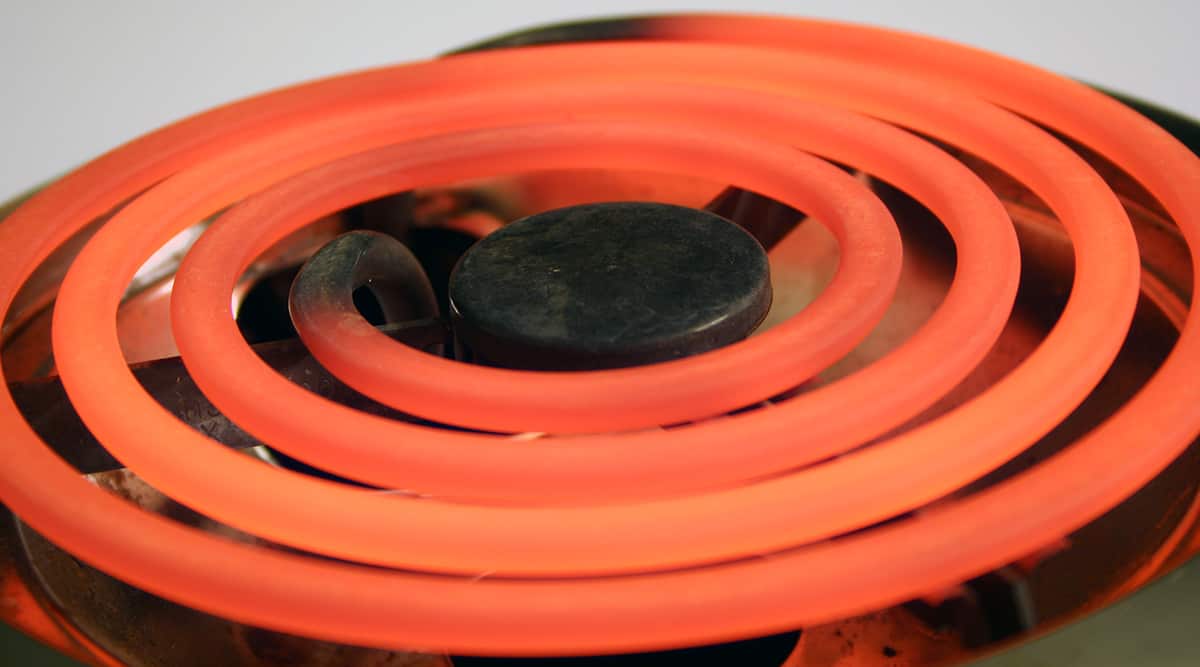

Electric stoves use electrical energy to generate heat. The heating element is typically a coil made of a special type of wire that resists the flow of electricity. This resistance causes the wire to heat up, and this heat is what cooks your food. The more electricity you allow to flow (by turning the knob higher), the hotter the stove eye gets.
Gas stove eyes
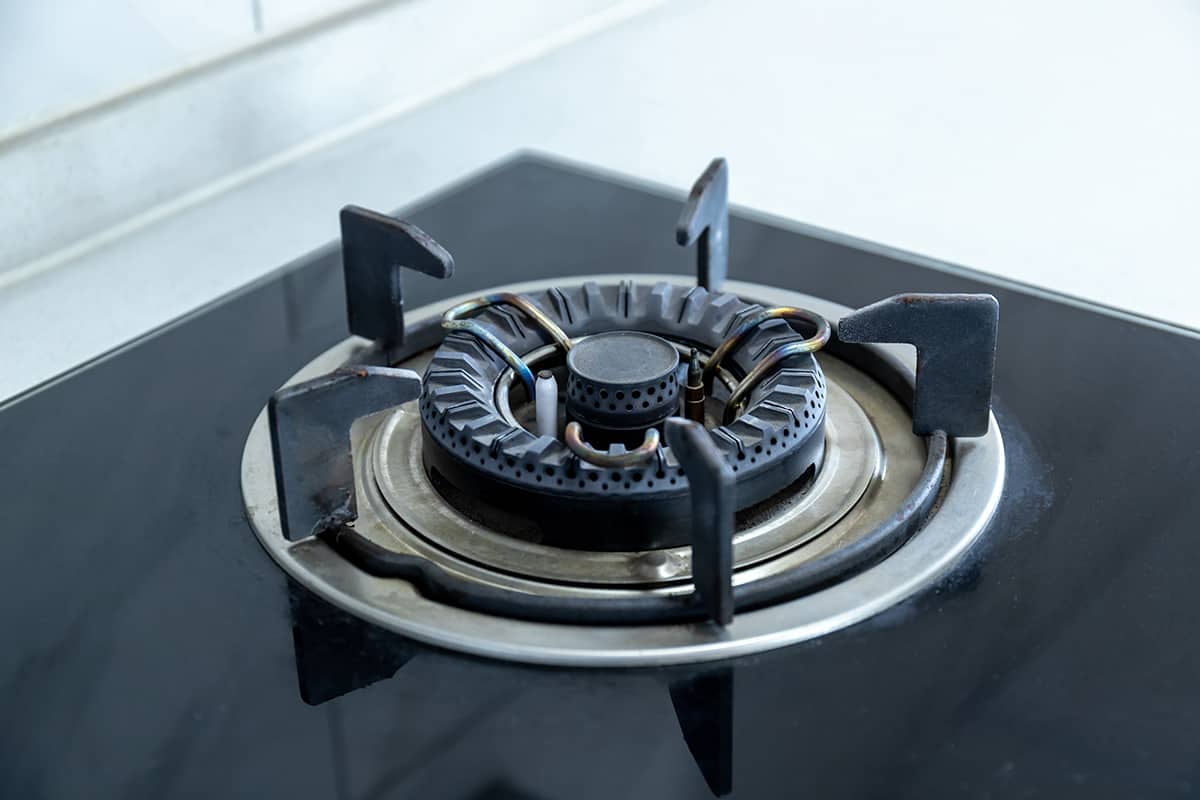

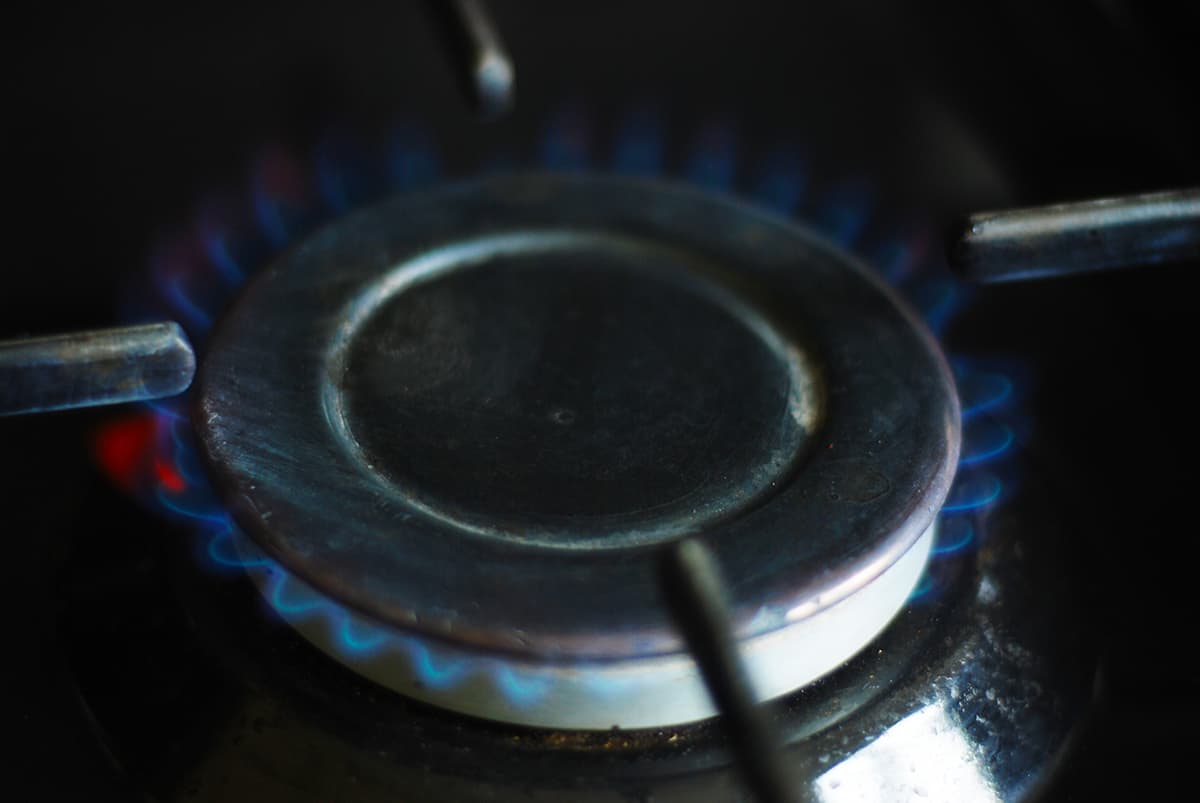
Gas stoves work differently than electric stoves. The burner has tiny holes that allow the gas to escape and mix with the air. When you light the stove, the gas-air mixture catches fire. The flames you see are actually the burning gas, and that’s what heats your pan and cooks your food.
Stove eye mechanisms
Heat from the stove eye needs to get to your food to cook it through a process called heat transfer, which occurs in three ways: conduction, convection, and radiation.
- Conduction is the process of heat transfer through direct contact. When your pan sits directly on the stove eye, the heat moves from the stove eye to the pan and then to the food.
- Convection is the transfer of heat through a fluid, which could be a liquid or a gas. In a range, this happens when the hot air rises and circulates around the oven, evenly cooking the food.
- Radiation is the transfer of heat in the form of waves or particles that can travel through space. In a stove, this happens when the heat radiates from the heating element or the flames to the pan.
Exploring the Components of a Stove Eye
A stove eye isn’t just one piece but a combination of several components, each performing a specific function. Let’s explore these essential parts of a stove eye.
1. Burner
The burner is the most visible part of the stove eye. It’s where all the magic happens! In an electric stove, the burner is the coiled element that glows red-hot when turned on. In a gas stove, the burner is the metal piece with several small holes where the flames emerge.
2. Heating element
The heating element is designed to withstand high temperatures without burning out quickly. However, over time and with continuous use, it may wear out and need replacement. You might notice this when the coil doesn’t heat evenly or doesn’t heat at all.
3. Control knob
In an electric stove, turning the knob adjusts a switch that controls the flow of electricity. The further you turn the knob, the more electricity flows, and the hotter the stove eye gets.
In a gas stove, the knob controls a valve that regulates the flow of gas. Turning the knob opens the valve more, allowing more gas to flow to the burner, and creating a larger flame.
The Different Types of Stove Eyes
Each type uses a unique method to generate heat for cooking, and each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s take a closer look at the four main types: electric coil, smooth top electric, gas, and induction stove eyes.
1. Electric coil stove eyes
Electric coil stoves are probably what you picture when you think of an electric stove. They have spiral-shaped burners, or “coils,” that heat up when electricity flows through them. When you place your pot or pan on the coil, the heat transfers to your cookware, allowing you to cook your food.
2. Smooth top electric stove eyes
Smooth top electric stoves, also known as ceramic or glass-top stoves, have a sleek, modern look. Instead of coils, they have heating elements hidden beneath a smooth ceramic or glass surface. When turned on, these elements heat the glass surface, which in turn heats your cookware.
3. Gas stove eyes
Gas stoves use natural gas or propane to generate heat. The gas flows to burners where it mixes with air and ignites, creating flames. The flames heat your cookware, allowing you to cook your food.
4. Induction stove eyes
Induction stoves represent the latest technology in cooking. Instead of using direct heat like the other types of stoves, induction stoves use a magnetic field to generate heat. When you place a pot or pan made of magnetic material on the induction burner, the magnetic field causes the pot itself to heat up.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Stove Eyes
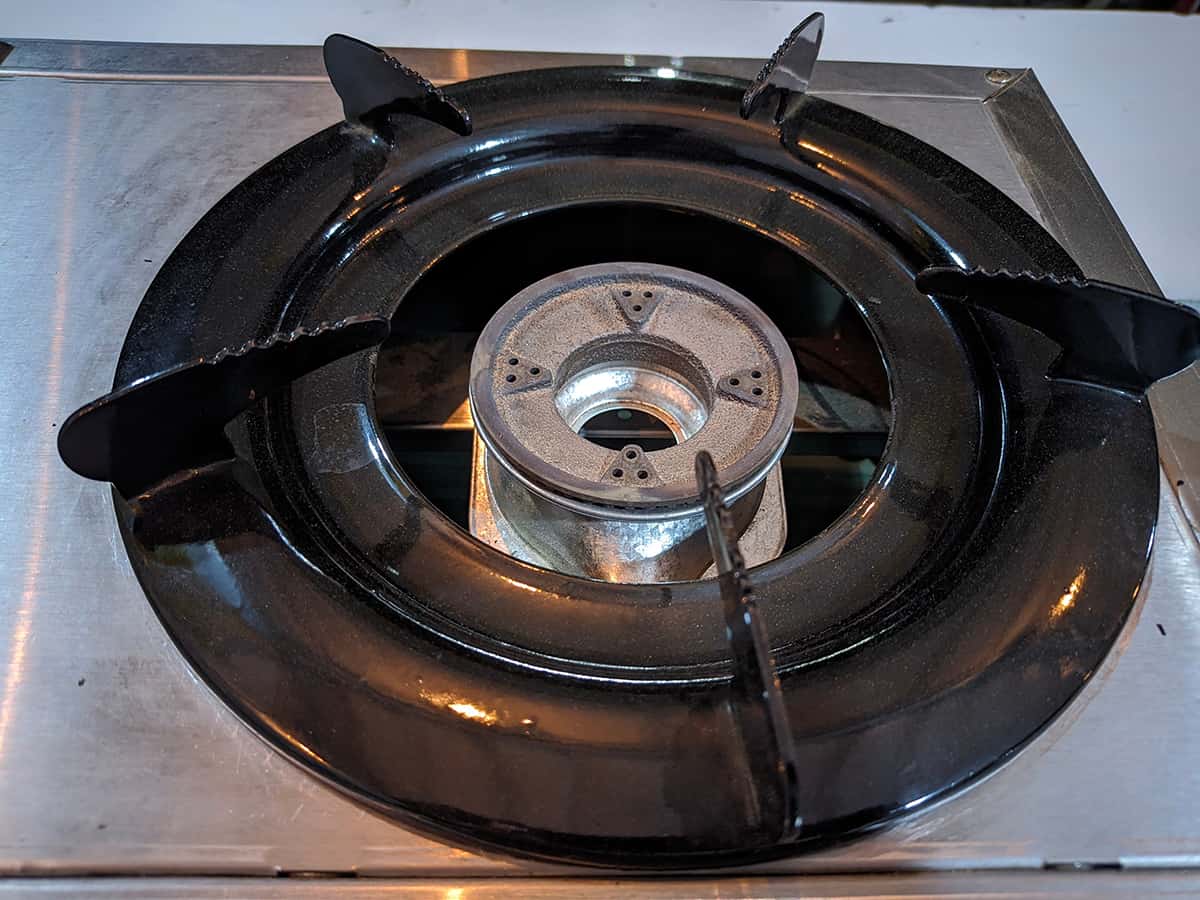

Your stove eye also needs regular maintenance. Let’s learn how to keep your stove eye in top shape and fix common problems.
Regular Maintenance of Your Stove Eye
A clean stove eye not only looks good but also works better and lasts longer. When food spills and builds up on the stove eye, it can cause uneven heating and even damage the burner.
- Electric stove eyes: To clean an electric coil stove eye, first make sure it’s cool and the stove is unplugged. Then remove the coil and the drip pan underneath. Soak them in warm soapy water, then scrub gently with a non-abrasive sponge to remove the food residues. Rinse, dry, and put them back on the stove.
- Gas stove eyes: For a gas stove eye, remove the grates and the burner caps. Soak them in warm soapy water and scrub gently. Use a pin or a toothpick to clear the small holes in the burner where the gas comes out. Rinse, dry, and replace the parts.
- Smooth top electric and induction stove eyes: These stoves can be cleaned with a simple wipe down with a damp cloth. For stubborn stains, use a cleaner designed specifically for glass or ceramic surfaces.
Proper maintenance can prevent many problems. This includes regular cleaning and checking the parts for wear and tear. If you notice the heating is uneven, the control knob is hard to turn, or the coil or burner is discolored or warped, it might be time for a replacement.
Troubleshooting Common Stove Eye Issues
Sometimes, despite your best maintenance efforts, your stove eye might not work as it should. Here are some common problems and solutions:
- The stove eye doesn’t heat: If your electric stove eye doesn’t heat, try replacing the burner. If it still doesn’t work, there might be a problem with the internal wiring or the switch, and you should call a professional. For a gas stove, clean the burner holes. If it still doesn’t light, the issue might be with the gas supply or the igniter.
- The stove eye heats unevenly: If your electric coil heats unevenly, it might be warped and need replacement. If a gas flame is orange or uneven, clean the burner holes.
- The control knob doesn’t turn: If the control knob is hard to turn or doesn’t turn at all, it might be worn out and need replacement.